Foot mycosis (ICD code 10 B35. 3) is a fungal infection of the skin on the feet caused by parasitic dermatophytes. It is found in about 20% of adults. Infection occurs through microtraumas, scratches, abrasions, wounds. Wet feet, diabetes and weakened immunity contribute to the development of the disease.
In people with endocrine disorders, in immunodeficiency conditions, the prevalence reaches 50%. More often, the disease progresses to a chronic form with alternating periods of remission and exacerbation. In 40-50% of cases mycosis causes onychomycosis or fungal infection of the nails.
Where and why does the infection occur?
Foot mycosis is a contagious disease that is easily transmitted through direct contact with a fungal carrier or household items. For example, in the shower through shoes, socks, towels, manicure materials, rubber items. In 70-95% of cases, the causative agent of foot mycosis is Trichophyton red (Tr. Rubrum).
Infection usually occurs in public places with high humidity where there are favorable conditions for the pathogen to multiply and spread. Such areas include swimming pools, public showers, saunas, water parks, gym dressing rooms. If a person infected with the fungus walks barefoot on the floor or carpets in the shower, it will leave infectious particles. And if a healthy person enters this place with bare feet, then the pathogen will fall on his skin. In this case, the fungus does not always appear immediately and causes the characteristic symptoms of the disease. With strong immunity, in the absence of health problems, a person remains only a carrier of infection, but at the same time he does not get sick.
Increased risk of fungal infections and mycosis of the feet increases:
. The first signs of the disease appear in the wrinkles between the fingers and from there extend to the plantar, lateral, posterior sides and nails.
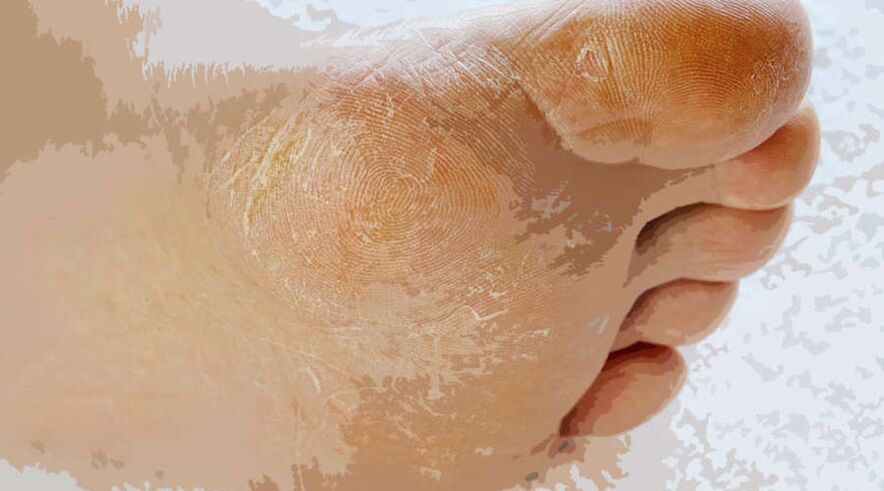
How my feet look with mycosis is shown in the photo.
Infection of the nails is accompanied by thickening, loss of gloss, blurring of the plate. The nail acquires a yellow, gray tint, becomes brittle, crumbles. Early clinical symptoms of foot mycosis include dryness, flaking of the skin, and painless cracking of the toes. This form of the disease is called deletion. Initially peeling and cracking does not cause pain, itching or discomfort. Only a doctor can notice the first unexplained signs of a fungal infection. In addition to erasure, there are other clinical forms of foot mycosis, each of which has its own symptoms.
Flat-footed
In the flat form of mycosis of the feet, the fingers appear between the toes and between the wrinkles. Usually no signs of inflammation are noted. There may be redness, damage to the nails, itching, thickening of the corneal layer, which brightens the skin. Papillary lines are more pronounced and the skin surface becomes dry, covered with lamellar scales. In this case the patient does not feel itching or other unpleasant sensations.
Hyperkeratotic
rash appears as a rash. The surface of the rash elements is covered with grayish-white layered scales. There is a detachment of epidermis, separate blisters. When combined, the rash forms indistinctly large foci that extend to the foot, including lateral, dorsal surfaces. With peeling foci marked hyperkeratosis or thickening of the skin. They look like calluses with cracks on top. In the hyperkeratotic form of mycosis of the feet, the affected area resembles the manifestations of psoriasis or eczema. The person suffers from dryness, itching and sometimes pain.
intertriginal
The intertriginal form of foot mycosis is similar to the symptoms of diaper rash. From here comes Lat. intertrigo - "diaper rash". More often, it acts on the skin at intervals of the third and fourth, fourth and fifth fingers. It becomes bright red, swollen. There are weeping wounds, deep, painful cracks. Unlike diaper rash, in intertriginous mycosis it is round with distinct contours, with a white outline along the edges of the epidermis. The person experiences itching, burning, pain. Dyzidrotic Dyzidrotic
Dyshidrotic forms of mycosis of the feet are characterized by multiple blisters of thick peak, mainly located in the arches. The rash spreads to large areas of the soles as well as to areas on the skin of the fingers and toes. Merge and create large bubbles. Wet erosion occurs at the site of the ruptured bladder. As the inflammation increases, the skin becomes red and swollen. At the stage of vesicle formation the patient feels unbearable itching.
Diagnosis
If you suspect mycosis, you need to see a dermatologist. To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor will examine the feet, asking what symptoms are bothering the person, how long ago and after which they appeared. Take a scratch from the affected area for microscopic analysis, cultural examination, to determine the specific type of pathogen. In addition, your doctor may order blood tests.
How to treat foot mycosis?
Mycologist or dermatologist refers to the treatment of foot skin mycosis. Depending on the clinical form of the disease, the severity of the lesion, visible changes, the doctor will select an adequate therapy.
A complication of a fungal infection on the feet can lead to an infection with a fungus on the hands. Mycosis of the feet sometimes causes secondary bacterial infections, especially when there are weeping wounds on the skin.
External fungicides (ointments, creams), tablets for oral administration are prescribed to fight fungi. Only topical therapy is effective in mild forms of foot mycosis. According to clinical guidelines, oral medications are prescribed in severe cases.
If necessary, anti-inflammatory, drying, antiseptic, anti-allergic drugs, agents that enhance the regeneration of damaged tissues. If there are signs of a bacterial infection, antibiotic therapy is prescribed.
Onychomycosis is the instrumental cleaning of fungus-infected areas. For further processing of nails are prescribed local antifungal agents: varnish, cream or ointment.
The duration of treatment is from two weeks to months. If not only the skin is affected but also the nails, the treatment is delayed. This is due to the fact that the nail grows slowly. To get rid of the infection it is necessary to restore a completely healthy nail plate.
Mycosis can be successfully treated while following your doctor's prescription. But if an improvement is noticed, the patient stops taking the medication, this causes the infection to return, turning it into a chronic form. It is necessary to complete the full course, even if the symptoms of the disease have already disappeared.
It is very important to treat mycosis of the feet, personal hygiene, diet, selection of comfortable shoes that do not damage the injured areas.
What should we do for prevention?
The following recommendations will help you to prevent or reduce the risk of developing foot and nail fungus: the limbs are weakened or the body's defenses are reduced;
If even a small peeling of the skin of the foot or cracks between the toes are found, it is worth testing for the fungus. Early diagnosis and timely treatment can help you avoid complications, extensive injury, discomfort, pain while walking, and getting a bacterial infection.































